

The main objectives are:
The depths for cold water pumping are also very much essential towards design of the cold water conduit. Even a coarse mapping of reasonable accuracy of temperatures and depths can lead to good resource assessment in individual region around the countries which are participating in the Annex.
Once each country puts together available information and carries out come additional measurements the data can be collated to use the country wise resource assessment towards a comprehensive Asian assessment
Progress achieved and difficulties faced would be brought out so that there is no necessity of reinventing the wheel. Future plan of OTEC activities in the various regions of the globe also is important to see the future roadmap.
Thus compilation of the status and future plan for OTEC in each country would be very beneficial for any further multi-country activities.
3. OTEC Economics
The main objective of this task is to understand the economics of OTEC. Capital Costs (CC) plus operations, maintenance, repair and replacement (OMR&R) costs, and financing will be addressed. Techno-commercial viability with associated spin-offs (tentatively listed below) will also be addressed. The second objective of this task is to develop an understanding of OTEC specialists from academia, research organizations, governments, and industry of varying expertise.
This Task is undertaken by different working groups (WG):
WG-1: Resource Assessment
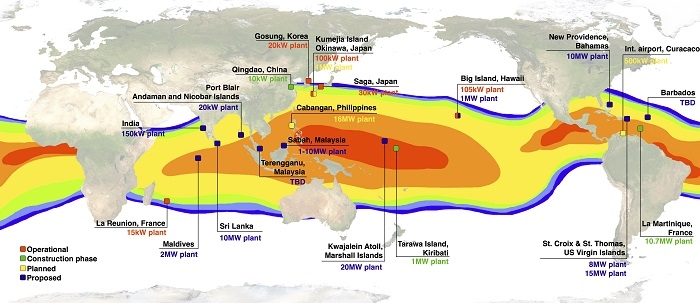
WG-2: Status and Plans
Final results will be presented in a workshop to work on the future road map.
WG-3: Economics on OTEC
Historical and current estimates of capital and operational costs associated with technically sound designs of closed cycle (CC) and open cycle (OC) OTEC plants will form the original data base for this project. These will be used to estimate the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) production under specific loan rate terms available from different sources ranging from commercial banks to concessionary loans from development banks. The LCOE provides the rate ($/kWh) required to breakeven over the assumed life of the plant. In the case of the OC-OTEC plant the combination of electricity rate ($/kWh) and desalinated water rate ($/m3) required to breakeven will be estimated. At this stage of development, when considering commercial loans, the investment rate of return would be given by a rate charged ($/kWh) above the LCOE.
This Tasks is carried out by Dr Luis Vega and Mr. Benjamin Martin from Xenesys, in collaboration with the IEA-OES Executive Committee.
In 2021 a White Paper on OTEC was released with a set of recommendations for the adoption of OTEC technology.
